General
The water which gets stored in the ground water reservoir through infiltration, percolation etc. is known as underground water. This water is generally pure, because it undergoes natural filtration during the percolation through soil pores. More over these waters are less likely to be contaminated by bacteria. However they are generally rich in dissolved salt, minerals, gases etc. Sometimes the ground water is brought to the surface by some natural source like springs, and sometimes these waters a; tapped by artificial means by constructing wells, infiltration galleries etc.
Occurrence of Ground water
All the materials of variable porosity near the upper portion of the earth’s crust are places of the potential storage for ground water. This storage of ground water is sometimes referred to as the Ground water Reservoir. . The possibility of occurrence of ground water mainly depends upon two properties of the underground soil, they are;
Porosity is the quantitative measurement of the voids present in the soil; which is the ratio of the volume of voids and the total volume given as a percentage. Porosity values of some common rock formation are as given below,
Permeability is defined as the ability of a rock or unconsolidated sediment to transmit or pass water through itself and is generally measured in terms of Coefficient of Permeability.
| Type of rock formation | Porosity | Coaff. Of Permeability
(cm/sec) |
| Granite, Quartzite | 1.5% | 0.000006 |
| Lime stone | 5 to 10% | 0.00004 |
| Sandstone | 10 to 15% | 0.004 |
| Sand and Gravel | 20 to 30% | 0.4 |
| Only Gravel | 25% | 4.0 |
| Only Sand | 35% | 0.04 |
| Clay and Soil | 45% | 0.0000004 |
Aquifers and Their Types
A permeable stratum or geological formation of permeable material, which is capable of yielding appreciable quantities of ground-water under gravity, Is known as an aquifer.
An aqulclude is an impermeable body of rock or stratum of sediment that acts as a barrier to the flow of groundwater.

(Aquifer and Aquicludes)
Aquifers vary in depth, lateral extent, and thickness; but in generally fall into one of the following two categories. The top most water bearing stratum having no confined Impermeable overburden (i.e. an aquiclude) laying over it, is known as Unconfined Aquifer or Non-artesian Aquifer.
When an aquifer Is confined in Its upper-and under surfaces, by impervious rock formations (i.e. aquiciudes), and is also broadly inclined so as to expose the aquifer somewhere to the catchment area at a higher level for the creation of sufficient hydraulic head, it is called Confined Aquifer or an Artesian Aquifer.
![clip_image003[5] clip_image003[5]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgr5NB1b-2nfdrYsSTeMbuG1lmqk-Df93m_thluAEgSFVpbBUYe3D9Fa84gnqIbzttZuFcxA4rdgYGSDHW964MbMjNWZeOSf4D1o7foII2w4ZNuo8vm_sCIDozgCcn__AXvZGR_nfztxt_g/?imgmax=800)
Non – artesian or Unconfined aquifer and well

Confined or Artesian aquifer and wells
Different Forms of Underground Sources
The underground water is generally available in the following forms.
Wells and Tube wells
Springs
Infiltration Wells
Infiltration Galleries
Wells and Tube Wells
Water well is a hole usually vertical, excavated in the earth for bringing ground water to the surface. The wells may be classified in two cases: i.e. Open Wells or Dug Wells and Tube Wells.
Open wells are generally open masonry wells having comparatively bigger diameters, and are suitable for low discharges say about 5 liters/sec or less. The diameters of open wells may vary from 1 to 9 meters, and are generally less than 20 meters In depth.
Tube Wells, which is sometimes called as deep wells, is a long pipe bored or drilled deep into the ground, intercepting one or more water bearing strata (aquifers). Generally deep wells are drilled to an aquifer below an impervious layer like clay. The water in deep tube wells gets purified due to natural filter, but is usually hard as it contained dissolved salts. They are generally 0.15 to 0.6 In diameter and may be deep as deep as 70 to 200 meters.
![clip_image002[1] clip_image002[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjgE1Co18mhKmAr0_O3Bhh7vdW9KmkciYPv0caTtwI2rLGYV-pD2e4NSnGtwjvb2WZ0TQZb9xfjI-b3Pd_uY-ebRHxnaRCXZWRjQAtM-dpZkfDOCv9NAzEfJtD98f0T67BSH6iLh7OveIMo/?imgmax=800)

A Strainer tube well
![clip_image004[1] clip_image004[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhzSoQ867bltuecdmYnLxkHyw_bjpDqYi3zEBQIhDFukNslanzKs7fwC1vk1lKLfiqYxBXpvRhRsdTZigOljAJl9dNKW1EYT2eljRIKM8fAOQLFI4U7o2WrZ3UHSI8f40QVf47hjqJweFGm/?imgmax=800)
Cavity type tube well

Cavity formation in Dig wells
Static Water Level Is the level at which water stands In a well in relation to the ground level. Draw Down is the extent to which the static water level Is reduced as a result of pumping. The draw down is also known as the depression of the water table. Cone of Depression is the solid cone formed between the water bearing stratum and the depressed water level In the well.
Springs
The natural outflow of ground water at the earth’s surface is said to form a spring. A pervious layer sandwiched between two impervious layers give rise to a natural spring. These are generally capable of supplying small amounts of water and are not considered as a good source of supply.
![clip_image002[3] clip_image002[3]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgAi_T3EmUXRgO4BK4dfK7ynCARpehE5nTlt0n78bRVQqY5JI-Fr26V5ujitySe9wdVwj9gbxmRozxyfSzFT3MaZWitBT3R7x2NTzncQjjFzmd8TyMOd0EmLcJ46UiFEHC2mHd1YoRhJ0Zy/?imgmax=800)
Gravity spring Artesian spring
Infiltration Wells
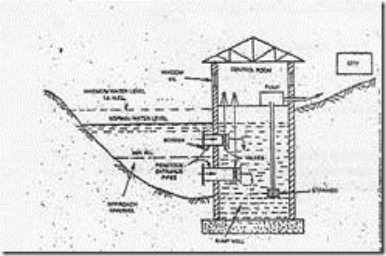
Infiltration wells are the shallow wells constructed In series along the bank of a river, In order to collect the river water seeping through their bottoms.
Infiltration Galleries
Infiltration galleries are the horizontal tunnels. Constructed at shallow depths such as 3 to 5 meters along the banks of rivers, through water bearing strata. They are sometimes called horizontal wells. These galleries are generally constructed of masonry walls with roof slabs, and extract water from the aquifer by various porous drain pipes. .
![clip_image003[5] clip_image003[5]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgG0iBRinolMBiLtK4-Th4kcSVweLpF9ffM9PEhaOzhdbi0ku4mIuJ1PyACjsb0j9n51SHqMq4b_kH9IjTTZ_ak94Iqh14sv2_SYwX7fYlJrwMeWUCzGy_TUX_pJDoFf0UB8KnRqYaLBUGv/?imgmax=800)
Artesian spring
Factors Governing the Selection of a Particular Source of Water
- Quantity of available water
- Quality of available water
- Distance of the source of supply
- General topography of the intervening area
- Elevation of the source of supply
![clip_image004[3] clip_image004[3]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEib1iV8biksiMy3O_BPlcCopyPDwP5A-K5KfWuEu6zi8MBdEmzzZe0nWUdCVo2M5pqRBKN2j0T8wtb_H0fklJv-xuKYpMLB-e7mD0GYLElosB7ZzmdBJuD13Fb5FF2nmco0WYUHj_skCdWF/?imgmax=800)
Location if infiltration wells Section of an Infiltration gallery
Labels: Waste Water Engineering

![clip_image003[5] clip_image003[5]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgr5NB1b-2nfdrYsSTeMbuG1lmqk-Df93m_thluAEgSFVpbBUYe3D9Fa84gnqIbzttZuFcxA4rdgYGSDHW964MbMjNWZeOSf4D1o7foII2w4ZNuo8vm_sCIDozgCcn__AXvZGR_nfztxt_g/?imgmax=800)

![clip_image002[1] clip_image002[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjgE1Co18mhKmAr0_O3Bhh7vdW9KmkciYPv0caTtwI2rLGYV-pD2e4NSnGtwjvb2WZ0TQZb9xfjI-b3Pd_uY-ebRHxnaRCXZWRjQAtM-dpZkfDOCv9NAzEfJtD98f0T67BSH6iLh7OveIMo/?imgmax=800)

![clip_image004[1] clip_image004[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhzSoQ867bltuecdmYnLxkHyw_bjpDqYi3zEBQIhDFukNslanzKs7fwC1vk1lKLfiqYxBXpvRhRsdTZigOljAJl9dNKW1EYT2eljRIKM8fAOQLFI4U7o2WrZ3UHSI8f40QVf47hjqJweFGm/?imgmax=800)

![clip_image002[3] clip_image002[3]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgAi_T3EmUXRgO4BK4dfK7ynCARpehE5nTlt0n78bRVQqY5JI-Fr26V5ujitySe9wdVwj9gbxmRozxyfSzFT3MaZWitBT3R7x2NTzncQjjFzmd8TyMOd0EmLcJ46UiFEHC2mHd1YoRhJ0Zy/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image003[5] clip_image003[5]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgG0iBRinolMBiLtK4-Th4kcSVweLpF9ffM9PEhaOzhdbi0ku4mIuJ1PyACjsb0j9n51SHqMq4b_kH9IjTTZ_ak94Iqh14sv2_SYwX7fYlJrwMeWUCzGy_TUX_pJDoFf0UB8KnRqYaLBUGv/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image004[3] clip_image004[3]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEib1iV8biksiMy3O_BPlcCopyPDwP5A-K5KfWuEu6zi8MBdEmzzZe0nWUdCVo2M5pqRBKN2j0T8wtb_H0fklJv-xuKYpMLB-e7mD0GYLElosB7ZzmdBJuD13Fb5FF2nmco0WYUHj_skCdWF/?imgmax=800)


![clip_image002[5] clip_image002[5]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjLoR0v3mu7HVz9FxcUNFghcowgm_BCzQdPS1MSvm2mH9O9CVH_0tv_RiNY6DulHXFRE6YwO2WTEUbRe_62uuliGil2NWWZeSCqmOY9d6oX9GH0OOe_oy-zDzTCIDZCh8Wkyq3QDuJ3kiZQ/?imgmax=800)

![clip_image002[6] clip_image002[6]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjvzOZc1DkmCSTLd8Efna7ILbKUDE1MfW9HklDkXFsY2r7KbNJA6M6WsEbRXtGsf6W1VtUvBiHlBE4ZLlh3gGe_DBq0_niYxF_2G3AwxaEeLr9bG8dXXgJz_d4eHSwVOXp6-7n_Usg6L6w2/?imgmax=800)
